Java 并发
多线程
多线程实现方式
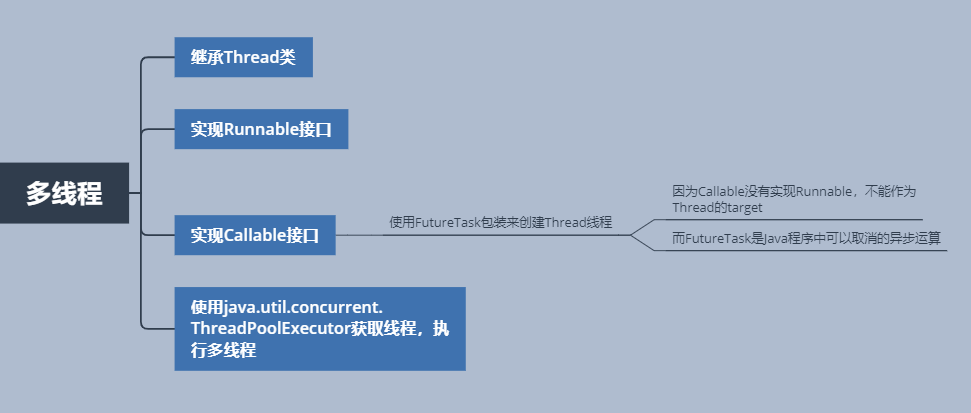
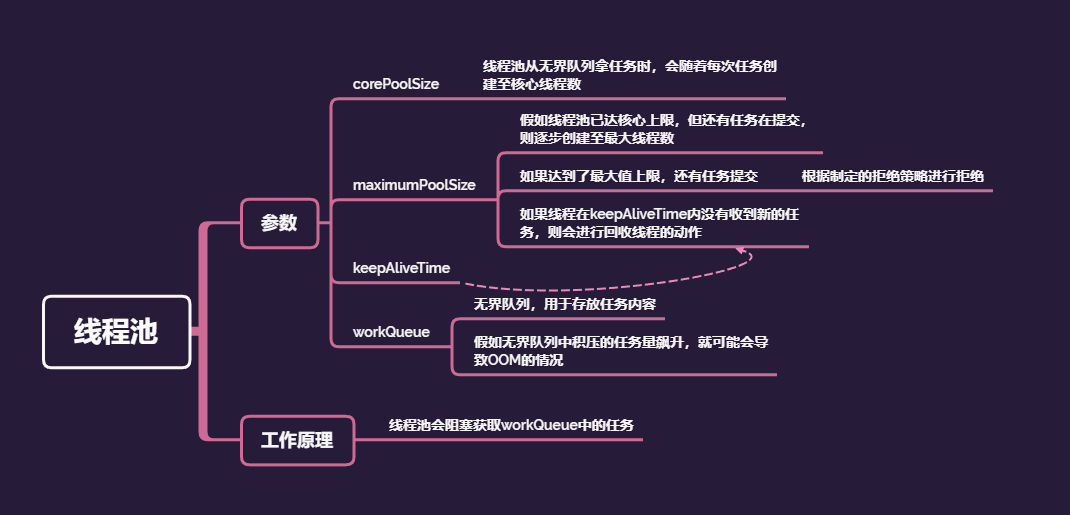
使用无界队列线程池 OOM 情况
// 创建无界队列
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
// 核心参数为以下内容
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
volatie
保证可见性和有序性,有序性主要是指防止指令重排(指令重排主要是指 jvm 优化时,可能会将未完全初始化的对象对外使用,即将指向 null 的对象对外使用,导致 NPE,而 volatie 避免了重排)
想了解 volatie 首先先了解 Java 线程内存模型
Java 线程内存模型
每个线程都有自己的工作内容,以及一个共享的主内存。
连环炮开始:
| 提问 | 答 |
|---|---|
| 为什么要让每个线程都用一个工作内存保留主内存的副本以供读取? | 如果每次线程都要 CPU 从主存中提取,导致性能差,主存的读写也极为麻烦,所以如果每个都配置,相当于高速的本地缓存,带来性能提升 |
| 每个线程自己拥有一份内存副本有什么问题? | 假如线程 1、线程 2 同时持有了 test=1 的值,这时线程 1 想改为 test=5,但是它只是改了自身副本的 1 为 5,没有改到主存以及线程 2 里面的内存副本 |
| 那么怎么解决上述的问题 | 加一个 volatie 标识变量,这样子每次修改时强制把最新的值刷回主内存,同时让其他线程的变量缓存直接失效过期,不允许再次读取和使用 |
graph TD;
线程1-->|修改变量指令test=5| 工作内存1
工作内存1--> | 修改完后强制刷回主存 test=5| 主内存
主内存-->|通知工作内存2 原test=1 过期 不准再使用| 工作内存2
工作内存2-->线程2
工作内存2-->|从主内存读取新变量值| 主内存
title[volatie可见性]
CAS
Compare And Set 比较后再设置
AtmoicInteger 原子类底层使用的不是以前的锁机制,而是无锁化的 CAS 机制,通过 CAS 机制保证了多线程修改一个数值的安全性。
大致流程:
graph TD;
线程--> |每个线程都获取变量值test=1| 变量
变量--> |线程做原子的CAS操作| CAS
CAS --> |如果比较时的值与获取的test=1一致,设置为累加1之后的状态|设置成功
CAS --> |如果比较时的值与获取的test=1不一致,重新获取新的变量|设置失败
设置失败-->|再次尝试CAS操作| CAS
title[CAS流程]
可以看到假如并发很严重时,会导致有很多线程一直自旋,可以上新家伙 LongAdder,大致原理是把 CAS 分散到一个 Cell 数组上,通过对 Cell 数值分组的 CAS 操作,提升了 CAS 总得效率,吞吐量。
当你需要当前累加总值时,会将 Cell 数组内的累加总值累加起来返回,但注意此处的 sum 函数不是互斥的,即不是准确的当前值。
/**
* Returns the current sum. The returned value is <em>NOT</em> an
* atomic snapshot; invocation in the absence of concurrent
* updates returns an accurate result, but concurrent updates that
* occur while the sum is being calculated might not be
* incorporated.
*
* @return the sum
*/
public long sum() {
Cell[] cs = cells;
long sum = base;
if (cs != null) {
for (Cell c : cs)
if (c != null)
sum += c.value;
}
return sum;
}
AQS
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 通过一个 state 的 int 变量记录加锁状态,以及一个记录当前线程是谁,实现可重入锁的关键功能。同时还有一个等待锁的队列,以及可重入锁的概念,当前线程可以反复上锁,即改变 state 的值直到 Integer.MAX_VAL
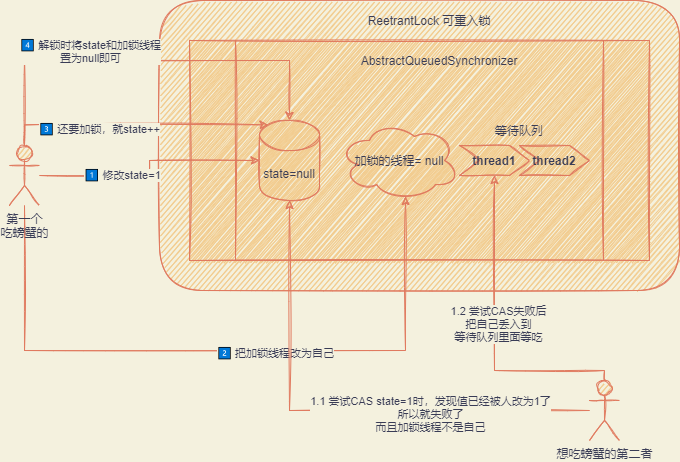
锁
公平锁
指加锁线程按照 FIFO 的顺序进行获取锁
非公平锁
像秒杀一样先到先得
ReentrantLock
以及大部分的并发包都是默认非公平策略的
也可以通过 new ReentrantLock(true)开启公平策略。
非公平的原理:
抢占锁时,不会管等待队列是否有线程,大家一起抢。
公平的原理:
抢占锁时,先看等待队列是否为空?如果不为空,则自觉插入到队列的尾部等待前面的线程处理完。
Condition
相对于Object monitor锁,这里实现的内容主要是通过Lock来实现await和signal内容
Condition
+await
+await
+awaitNanos
+awaitUninterruptibly
+awaitUntil
+signal
+signalAll
线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
| key | val |
|---|---|
| corePoolSize | 核心线程,哪怕当前状态为 idle 闲置,也会保留,除非定义了 allCoreThreadTimeOut |
| maximumPoolSize | 最大线程数 |
| keepAliveTime | 当线程数大于核心线程时,闲置的线程如果超过了等待时间则会 kill 掉 |
| workQueue | 持有着即将执行的工作队列。只会持有通过 execute()提交的 Runnable 的任务 |
| threadFactory | 通过线程工厂创建新的线程 |
| handler | 当执行阻塞时,比如说线程池满了,等待队列满了,这时应选的拒绝策略 |